Recently, Wu Jinjun, Su Youlu and Feng Juan from the South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Aquatic Sciences have made new progress in the distribution and epidemiology of drug-resistant bacteria (ARB) and drug-resistant genes (ARGs) in cage culture areas of marine fish in Hainan Province. The articles such as Prevalence and distribution of antibiotic resistance in marine fish farming areas in Hainan, China; Diversity and abundance of antibiotic resistance of bacteria during the seedling period in marine fish cage-culture areas of Hainan, China; etc. were published in the internationally renowned journals such as Science of the Total Environment and Marine Pollution Bulletin.
This series of studies focused on the diversity and abundance distribution of drug-resistant bacteria (ARB) and drug-resistant genes (ARGs) in marine cage culture areas of Hainan Province. The correlation between ARB, ARGs and environmental factors was explored by network analysis and redundancy analysis. The results show that salinity was negatively correlated with most ARBs and ARGs abundances, and some ARBs were significantly correlated with ARGs. Ruegeria and tetB were the biological indicators of most ARBs and ARGs, respectively. This indicated that ARB and ARGs had some interaction mechanism in mariculture cages.
Get links online for papers:
Https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X19301699
Https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969718341470

Advances in the epidemiology and distribution of drug-resistant bacteria (ARB) and drug-resistant genes (ARGs) in cage culture in Hainan have been achieved by South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute
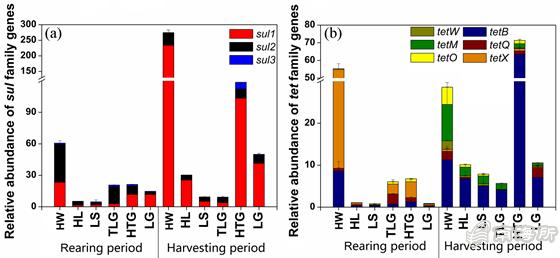
Relative abundance of ARGs in sea cage aquaculture area, hainan province
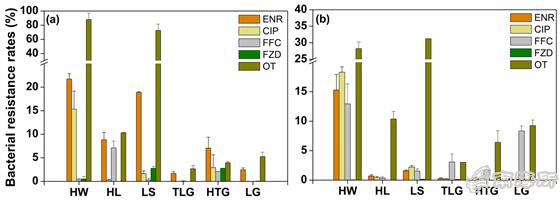
Bacterial drug resistance rate in seawater cage culture area of hainan province

